Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. During the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries, a number of arsenic compounds have been used as medicines; copper acetoarsenite was used as a green pigment known under many different names. Arsenic in the environment. Arsenic can be found naturally on earth in small concentrations.
Arsenic Windows 10 install remote desktop.
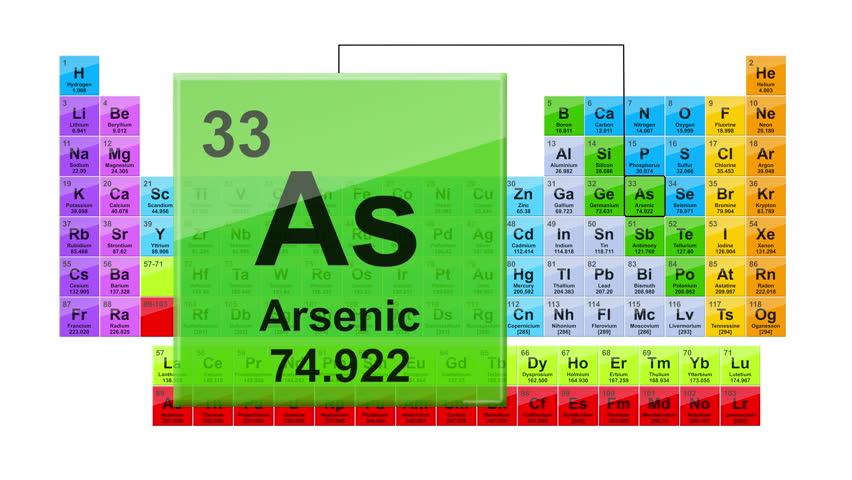
| Name | Arsenic |
| Symbol | As |
| Atomic Number | 33 |
| Atomic Mass | 74.9216 atomic mass units |
| Number of Protons | 33 |
| Number of Neutrons | 42 |
| Number of Electrons | 33 |
| Melting Point | 817.0° C |
| Boiling Point | 613.0° C |
| Density | 5.72 grams per cubic centimeter |
| Normal Phase | Solid |
| Family | Metalloids |
| Period | 4 |
| Cost | Unavailable |

| Origin of Name | From the Greek word 'arsenikos' and the Latin word 'arsenicum,' meaning yellow orpiment |
| Date and Place of Discovery | It's been used since ancient times, but the first recorded use was in 1250 when Albert the Great, an alchemist, heated a compound containing arsenic. |
| Discovered by | Albert the Great aka Albertus Magnus |
| Common Compounds |
|
| Interesting facts |
|
| Common Uses |
|
Photo Courtesy of About.com |
| Arsenic Atomic Structure | Elements by Name | Elements by Number | Home |
Element Arsenic - As
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Arsenic is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Arsenic. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Arsenic Menu
- Arsenic Page One
- Arsenic Page Two
- Arsenic Page Three
Overview of Arsenic
- Atomic Number: 33
- Group: 15
- Period: 4
- Series: Metalloids (Nonmetal)
Arsenic's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Arsenicum
- Czech: Arzen
- Croatian: Arsen
- French: Arsenic
- German: Arsenic - r
- Italian: Arsenico
- Norwegian: Arsen
- Portuguese: Arsênio
- Russian: Мышьяк
- Spanish: Arsénico
- Swedish: Arsenik

Atomic Structure of Arsenic
- Atomic Radius: 1.33Å
- Atomic Volume: 13.1cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 1.2Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)σa/barns: 4.3
- Crystal Structure: Rhombohedral
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p6 3s2p6d10 4s2p3
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,8,18,5
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius: 0.58Å
- Filling Orbital: 4p3
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 33
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 42
- Number of Protons: 33
- Oxidation States:±3,5
- Valence Electrons: 4s2p3
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Arsenic
- Electrochemical Equivalent: 0.93177g/amp-hr
- Electron Work Function: 3.75eV
- Electronegativity: 2.18 (Pauling); 2.2 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 369.9kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- halogenated compounds, rhubidium, carbide
- Ionization Potential
- First: 9.81
- Second: 18.633
- Third: 28.351
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV): 74
Physical Properties of Arsenic
- Atomic Mass Average: 74.92159
- Boiling Point: 876K 603°C 1117°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: 4.7E-6
- Conductivity
- Electrical: 0.0345 106/cm Ω
Thermal: 0.502 W/cmK
- Electrical: 0.0345 106/cm Ω
- Density: 5.72g/cc @ 300K
- Description:
- Gray brittle non-metal flakes.
- Enthalpy of Atomization: 301.3 kJ/mole @ 25°C
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 24.44 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 34.76 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class:
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Hardness Scale
- Brinell: 1440 MN m-2
- Mohs: 3.5
- Heat of Vaporization: 34.76kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 1081K 808°C 1486°F
- Molar Volume: 13.08 cm3/mole
- Optical Refractive Index: 1.001552
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Solid
- Specific Heat: 0.33J/gK
Regulatory / Health
- CAS Number
- 7740-38-2
- UN/NA ID and ERG Guide Number
- UN1557
- RTECS: CG0525000
- NFPA 704
- Health: 3
- Fire: 2
- Reactivity:
- Special Hazard:
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- TWA: 0.5 mg/m3
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- No limits set by NIOSH
- Routes of Exposure: Inhalation; Ingestion; Skin and/or eye contact
- Target Organs: Skin, respiratory system, kidneys, central nervous system, liver, gastrointestinal tract, reproductive system
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 0.0017-0.09
- Bone/p.p.m: 0.08-1.6
- Liver/p.p.m: 0.023-1.61
- Muscle/p.p.m: 0.009-0.65
- Daily Dietary Intake: 0.04-1.4 mg
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 0.5-15 mg
Who / Where / When / How
- Discoverer: Alberts Magna
- Discovery Location: Unknown
- Discovery Year: 1250
- Name Origin:
- Greek: arsenikos (male); Latin: arsenicum.
- Abundance of Arsenic:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 1.5
- Seawater/p.p.m.:
- Atlantic Suface: 0.00145
- Atlantic Deep: 0.00153
- Pacific Surface: 0.00145
- Pacific Deep: 0.00175
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: N/A
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): N/A
- Sources of Arsenic:
- Found in mispickel (arsenopyrite). Mainly produced as a by-product of refining certain sulfide ores. Annual world wide production is around 47,000 tons (As2O3).
- Uses of Arsenic:
- Used as a deadly poison, in shotgun pellets, metal for mirrors, glass, lasers, light-emitting diodes (LED) and in semiconductors.
- Additional Notes:
- Arsenic is a carcinogen, associated with lung cancer when inhaled. Contact with skin can result in skin cancer. Also damage to intestines and liver. Toxic when ingested. Found in pesticides and wood preservatives. It is naturally occurring in many household products. It may have been known to ancient civilizations, but was probably first isolated by Magnus who lived between 1193-1280. Many sources reference 1250 as the year of discovery but this may be speculation.
Arsenic Menu
- Arsenic Page One
- Arsenic Page Two
- Arsenic Page Three
References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.

Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:

Free youtube download video for mac. Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Arsenic - As. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/25/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/As.html
.
Linking to this page
Symbol And Atomic Number Of Arsenic
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
<a href='https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/As.html'>echo Periodic Table of Elements: Arsenic - As (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)</a>- Comprehensive information for the element Arsenic - As is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
Atomic Number Of Arsenic-75
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it.

